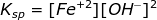Category: Chemical Engineering Math
"Published in Newark, California, USA"
Calculate
the pH of a liter of solution that contains 0.1 mole of acetic acid and
0.1 mole of sodium acetate. If few drops of concentrated hydrochloric acid is added to the
solution that would make the solution 0.02 M in HCl if the buffer was
not present, what is the new pH of the solution?
Solution:
A
buffer solution is a solution of weak acid and its salt or a solution
of weak base and its salt. The purpose of making a buffer solution is to
prevent the rapid change of pH if more acid or base is added to the
solution.
Since acetic acid is a weak acid, then it is partially ionized into acetate ion and hydrogen ion as follows
In a liter of solution at equilibrium,
where x is moles of HC2H3O2 that partially ionized. The ionization constant for HC2H3O2 is given by the equation
From Table of Ionization Constants of Acids and Bases, Ka = 1.8 x 10-5 for acetic acid. The amount of HC2H3O2 that partially ionized is
If
0.1 moles of sodium acetate which is completely ionized into 0.1 moles
of sodium ion and 0.1 moles of acetate ion is added to the solution,
then the above equation becomes
The acetate ion from sodium acetate will be added to the acetate ion from acetic acid. Since the value of Ka is less than 1 x 10-3, then we can neglect x at the numerator and denominator as follows
Hence, the concentration of hydrogen ion is
Therefore, the pH of a buffer solution is
If few drops of concentrated hydrochloric acid is added to buffer solution, then acetate ion will react with hydrogen ion from hydrochloric acid to form acetic acid. The amount of acetic acid will increase while the amount of acetate ion will decrease. From the equation of buffer solution
if
0.02 M HCl solution or 0.02 moles of concentrated HCl is added and
assuming that the increase in volume of solution is negligible, then the
above equation becomes
Since the value of Ka is less than 1 x 10-3, then we can neglect x at the numerator and denominator as follows
Hence, the concentration of hydrogen ion is
Therefore, the pH of final solution is
As
you can see that there's a slight change of pH of buffer solution after
the addition of few drops of concentrated hydrochloric acid. Without buffer solution, the
pH of 0.02 M HCl solution is 1.70.
Category: Chemical Engineering Math
"Published in Newark, California, USA"
Calculate the pH of a liter of solution that contains 0.1 mole of acetic acid and 0.1 mole of sodium acetate. If sodium hydroxide pellets is added to the solution that would make the solution 0.02 M in NaOH if the buffer was not present, what is the new pH of the solution?
Solution:
A buffer solution is a solution of weak acid and its salt or a solution of weak base and its salt. The purpose of making a buffer solution is to prevent the rapid change of pH if more acid or base is added to the solution.
Since acetic acid is a weak acid, then it is partially ionized into acetate ion and hydrogen ion as follows
In a liter of solution at equilibrium,
where x is moles of HC2H3O2 that partially ionized. The ionization constant for HC2H3O2 is given by the equation
From Table of Ionization Constants of Acids and Bases, Ka = 1.8 x 10-5 for acetic acid. The amount of HC2H3O2 that partially ionized is
If 0.1 moles of sodium acetate which is completely ionized into 0.1 moles of sodium ion and 0.1 moles of acetate ion is added to the solution, then the above equation becomes
The acetate ion from sodium acetate will be added to the acetate ion from acetic acid. Since the value of Ka is less than 1 x 10-3, then we can neglect x at the numerator and denominator as follows
Hence, the concentration of hydrogen ion is
Therefore, the pH of a buffer solution is
If sodium hydroxide pellets is added to buffer solution, then acetic acid will react with sodium hydroxide to form sodium acetate. The amount of acetic acid will decrease while the amount of acetate ion will increase. From the equation of buffer solution
if 0.02 M NaOH solution or 0.02 moles of NaOH pellets is added and assuming that the increase in volume of solution is negligible, then the above equation becomes
Since the value of Ka is less than 1 x 10-3, then we can neglect x at the numerator and denominator as follows
Hence, the concentration of hydrogen ion is
Therefore, the pH of final solution is
As you can see that there's a slight change of pH of buffer solution after the addition of sodium hydroxide pellets. Without buffer solution, the pH of 0.02 M NaOH solution is 12.30.
Category: Chemical Engineering Math
"Published in Newark, California, USA"
The pH of a saturated solution of Fe(OH)2 is 9.30. Calculate the Ksp of Fe(OH)2.
Solution:
If the pH of Fe(OH)2 is 9.30, then the pOH is
The concentration of hydroxide ion in molarity is
Take the inverse logarithm on both sides of the equation, we have
Since Fe(OH)2 is slightly soluble in water, then the ionization of Fe(OH)2 is
By using mole to mole relationship of the reactants and products in a liter of solution, if
then it follows that
Therefore, the solubility product constant of Fe(OH)2 is