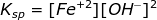Category: Chemical Engineering Math
"Published in Newark, California, USA"
The pH of a saturated solution of Fe(OH)2 is 9.30. Calculate the Ksp of Fe(OH)2.
Solution:
If the pH of Fe(OH)2 is 9.30, then the pOH is
The concentration of hydroxide ion in molarity is
Take the inverse logarithm on both sides of the equation, we have
Since Fe(OH)2 is slightly soluble in water, then the ionization of Fe(OH)2 is
By using mole to mole relationship of the reactants and products in a liter of solution, if
then it follows that
Therefore, the solubility product constant of Fe(OH)2 is
This website will show the principles of solving Math problems in Arithmetic, Algebra, Plane Geometry, Solid Geometry, Analytic Geometry, Trigonometry, Differential Calculus, Integral Calculus, Statistics, Differential Equations, Physics, Mechanics, Strength of Materials, and Chemical Engineering Math that we are using anywhere in everyday life. This website is also about the derivation of common formulas and equations. (Founded on September 28, 2012 in Newark, California, USA)
Tuesday, September 23, 2014
Monday, September 22, 2014
Solving for pH of a Base Problems
Category: Chemical Engineering Math
"Published in Newark, California, USA"
Calculate the pH for
(a) 0.02 M NaOH
(b) 0.10 M NH4OH
Solution:
pH means "power of hydrogen". Some chemists say that pH means "potential of hydrogen". It is a measurement of acidity or alkalinity of a solution and it has a scale from 0 to 14. If pH is ranging from 0 to 6, then the solution is acidic. If pH is 7, then the solution is neutral like water, for example. If pH is ranging from 8 to 14, then the solution is alkaline. The pH of any acidic solution can be calculated by using the equation,
where [H+] is the concentration of hydrogen ion in molarity.
The pOH of any basic solution is
where [OH-] is the concentration of hydroxide ion in molarity.
Hence, the pH of any basic solution can be calculated by using the equation,
or
(a) For 0.020 M NaOH solution
Since NaOH is a strong base, then it is completely ionized into sodium ion and hydroxide ion as follows
In a liter of solution, 0.02 moles of NaOH is ionized completely into 0.02 moles of Na+ and 0.02 moles of OH-. Hence, the concentration of [OH-] is 0.02.
The pOH of 0.02 M NaOH is
Therefore, the pH of 0.02 M NaOH is
If the pH of a base is closer to 14, then it is a strong base.
(b) For 0.10 M NH4OH solution
Since NH4OH is a weak base, then it is partially ionized into ammonium ion and hydroxide ion as follows
In a liter of solution at equilibrium,
where x is moles of NH4OH that partially ionized. The ionization constant for NH4OH is given by the equation
From Table of Ionization Constants of Acids and Bases, Kb = 1.8 x 10-5 for ammonium hydroxide. The amount of NH4OH that partially ionized is
Since the value of Kb is less than 1 x 10-3, then we can neglect x at the denominator as follows
Hence, the concentration of hydroxide ion is
The pOH of 0.01 M NH4OH is
Therefore, the pH of 0.01 M NH4OH is
If the pH of a base is closer to 7, then it is a weak base.
"Published in Newark, California, USA"
Calculate the pH for
(a) 0.02 M NaOH
(b) 0.10 M NH4OH
Solution:
pH means "power of hydrogen". Some chemists say that pH means "potential of hydrogen". It is a measurement of acidity or alkalinity of a solution and it has a scale from 0 to 14. If pH is ranging from 0 to 6, then the solution is acidic. If pH is 7, then the solution is neutral like water, for example. If pH is ranging from 8 to 14, then the solution is alkaline. The pH of any acidic solution can be calculated by using the equation,
where [H+] is the concentration of hydrogen ion in molarity.
The pOH of any basic solution is
where [OH-] is the concentration of hydroxide ion in molarity.
Hence, the pH of any basic solution can be calculated by using the equation,
or
(a) For 0.020 M NaOH solution
Since NaOH is a strong base, then it is completely ionized into sodium ion and hydroxide ion as follows
In a liter of solution, 0.02 moles of NaOH is ionized completely into 0.02 moles of Na+ and 0.02 moles of OH-. Hence, the concentration of [OH-] is 0.02.
The pOH of 0.02 M NaOH is
Therefore, the pH of 0.02 M NaOH is
If the pH of a base is closer to 14, then it is a strong base.
(b) For 0.10 M NH4OH solution
Since NH4OH is a weak base, then it is partially ionized into ammonium ion and hydroxide ion as follows
In a liter of solution at equilibrium,
where x is moles of NH4OH that partially ionized. The ionization constant for NH4OH is given by the equation
From Table of Ionization Constants of Acids and Bases, Kb = 1.8 x 10-5 for ammonium hydroxide. The amount of NH4OH that partially ionized is
Since the value of Kb is less than 1 x 10-3, then we can neglect x at the denominator as follows
Hence, the concentration of hydroxide ion is
The pOH of 0.01 M NH4OH is
Therefore, the pH of 0.01 M NH4OH is
If the pH of a base is closer to 7, then it is a weak base.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)