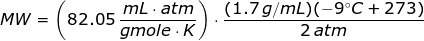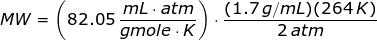"Published in Newark, California, USA"
The following data were obtained in the determination of a HC gas containing 92.3% C by weight at -9°C at various pressure:
| P (atm) | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| ρ (g/mL) | 1.45 | 1.7 | 1.95 |
Identify the gas.
Solution:
The given problem is about finding the molecular formula of a hydrocarbon gas using the principles of empirical and molecular formula. Since the given items are temperature, pressure, and density, then we have to use the Ideal Gas Law in order to get the molecular weight at different pressures and densities.
Let's consider the Ideal Gas Law equation:
but

and the above equation becomes
but

Hence, the Ideal Gas Law equation if the density is given is
where:
MW = molecular weight of unknown gas
ρ = is the density of unknown gas
R = universal gas law constant
T = absolute temperature of unknown gas
P = pressure of unknown gas
Since the units like K, mL, grams, gmoles, and atm are given,then the value of universal gas law constant is

Looking at the given table above, if you get the average of the given pressures and densities, then the value of P is 2 atm and the value of ρ is 1.7 g/mL.
The molecular weight of the unknown gas is
In one mole of unknown gas, the weight of C is
and the weight of H is
The number of moles of C is
and the number of moles of H is
In order to get the number of atoms of C and H, we need to divide them with the smallest number of moles. In this case, H has a number of smallest moles.
The number of C atoms is
and the number of H atoms is
Hence, the empirical formula of the unknown gas is CH.
Since CH is not a stable molecule, then we have to multiply both the number of C and H atoms by 2 in order to become a stable molecule. If you will follow the Octet Rule and Covalent Bonding, the number of electrons surrounding at each C atoms will be equal to eight.
Therefore, the molecular formula of the unknown gas is C2H2 which is acetylene.